Upper GI
Pancreatic Cancer
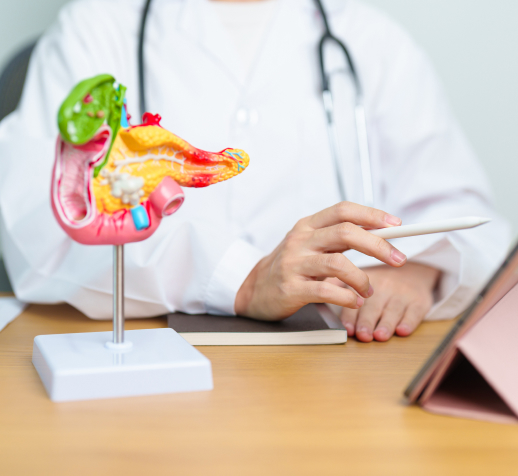
Pancreatic cancer begins in the tissues of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach that plays an essential role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. Early detection is challenging, and symptoms often appear at advanced stages.
Types of Pancreatic Cancer
Exocrine Tumours
The most common type, usually adenocarcinoma, which begins in the ducts of the pancreas.
Endocrine Tumours
Also known as pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (NETs), these are less common and arise from hormone-producing cells.
Risk Factors
Age
Most cases occur in people over 65.
Gender
Men are slightly more likely to develop pancreatic cancer.
Smoking
A significant risk factor.
Diabetes
Long-standing diabetes can increase the risk.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Long-term inflammation of the pancreas.
Family History
Genetics play a role; having a family history of pancreatic cancer increases risk.
Obesity
Being overweight is a risk factor.
Diet
High intake of red and processed meats.
SYMPTOMS
Jaundice
Yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, and pale stools.
Abdominal Pain
Often radiates to the back and can be persistent.
Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss and loss of appetite.
Nausea and Vomiting
Frequent and severe.
New-Onset Diabetes
Particularly in older adults.
Digestive Problems
Including indigestion, diarrhea, and changes in stool.
Blood Clots
In legs (deep vein thrombosis) or other areas.
DIAGNOSIS
Imaging Tests
CT scan, MRI, and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) to visualize the pancreas.
Blood Tests
CA 19-9 is a tumour marker that may be elevated in pancreatic cancer.
Biopsy
Obtaining a tissue sample for analysis, often guided by imaging.
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Combines endoscopy and X-ray to examine the bile and pancreatic ducts.
Trusted for care
Dr Wang and his team are respected and trusted for the care provided to their patients
Treatment Options
Surgery
Whipple Procedure (Pancreaticoduodenectomy)
Removes the head of the pancreas, part of the small intestine, gallbladder, and bile duct.
Distal Pancreatectomy
Removes the body and tail of the pancreas, often with the spleen
Total Pancreatectomy
Removes the entire pancreas, part of the stomach, part of the small intestine, the common bile duct, the gallbladder, the spleen, and nearby lymph nodes
Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
Targets the tumour with high-energy rays.
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT)
Delivers high doses of radiation precisely to the tumour.
Chemotherapy
Drugs
Such as gemcitabine, fluorouracil (5-FU), irinotecan, and oxaliplatin.
Combination Therapy
Often used with radiation or other drugs.
Targeted Therapy
Erlotinib (Tarceva)
Targets specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth.
Immunotherapy
Checkpoint Inhibitors
Such as pembrolizumab for tumours with specific genetic changes.
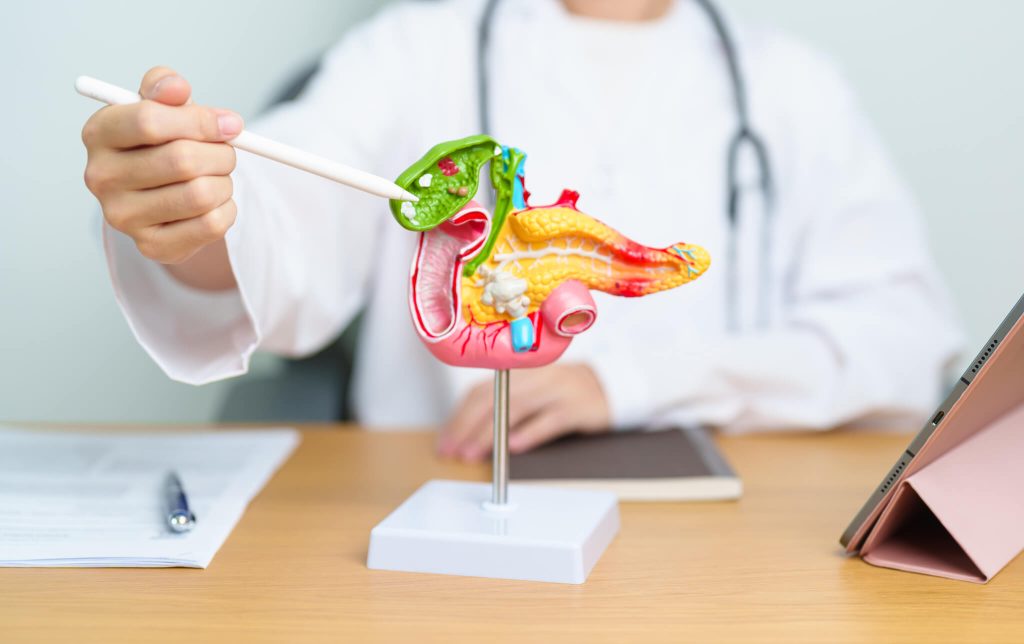
Palliative Care
Focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life. This can include pain management, nutritional support, and addressing digestive issues.
Prognosis
The prognosis for pancreatic cancer is generally poor due to late diagnosis. However, early-stage detection and advances in treatment are improving outcomes
Living with Pancreatic Cancer
Regular Monitoring
Follow-up appointments and imaging tests to monitor treatment response and detect any recurrence.
Nutritional Support
Working with a dietitian to manage symptoms and maintain weight.
Pain Management
Medications and procedures to manage pain.
Emotional Support
Counselling, support groups, and mental health care to cope with the emotional impact of the disease.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- New or worsening symptoms.
- Severe abdominal or back pain.
- Signs of jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes).
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Changes in diabetes management.

Other Upper GI Conditions
Medical procedure used to examine the upper part of the GI Tract, colon and rectum for abnormalities….
Also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining…
Also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining…

Also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining…
