Upper GI
Gastric Cancer
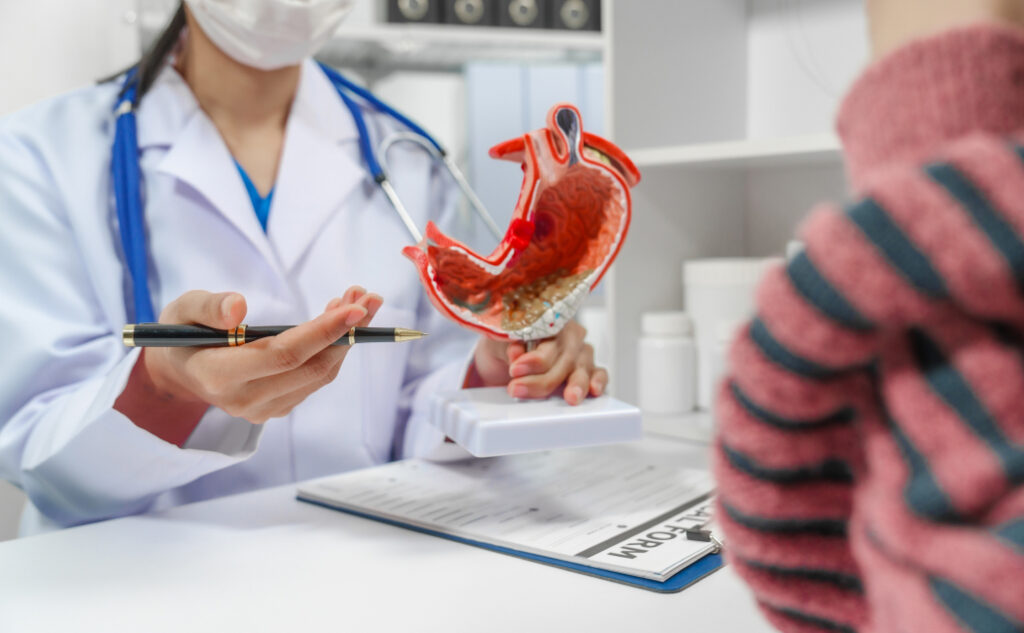
Gastric cancer, also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. It can develop in any part of the stomach and may spread to other organs.
Types of Gastric Cancer
Types of Gastric Cancer
The most common type, originating in the glandular cells of the stomach lining.
Lymphoma
Cancer of the immune system tissue found in the stomach.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour (GIST)
A rare type of cancer that forms in the interstitial cells of Cajal in the stomach wall.
Carcinoid Tumour
A slow-growing tumour that originates in hormone-producing cells of the stomach.
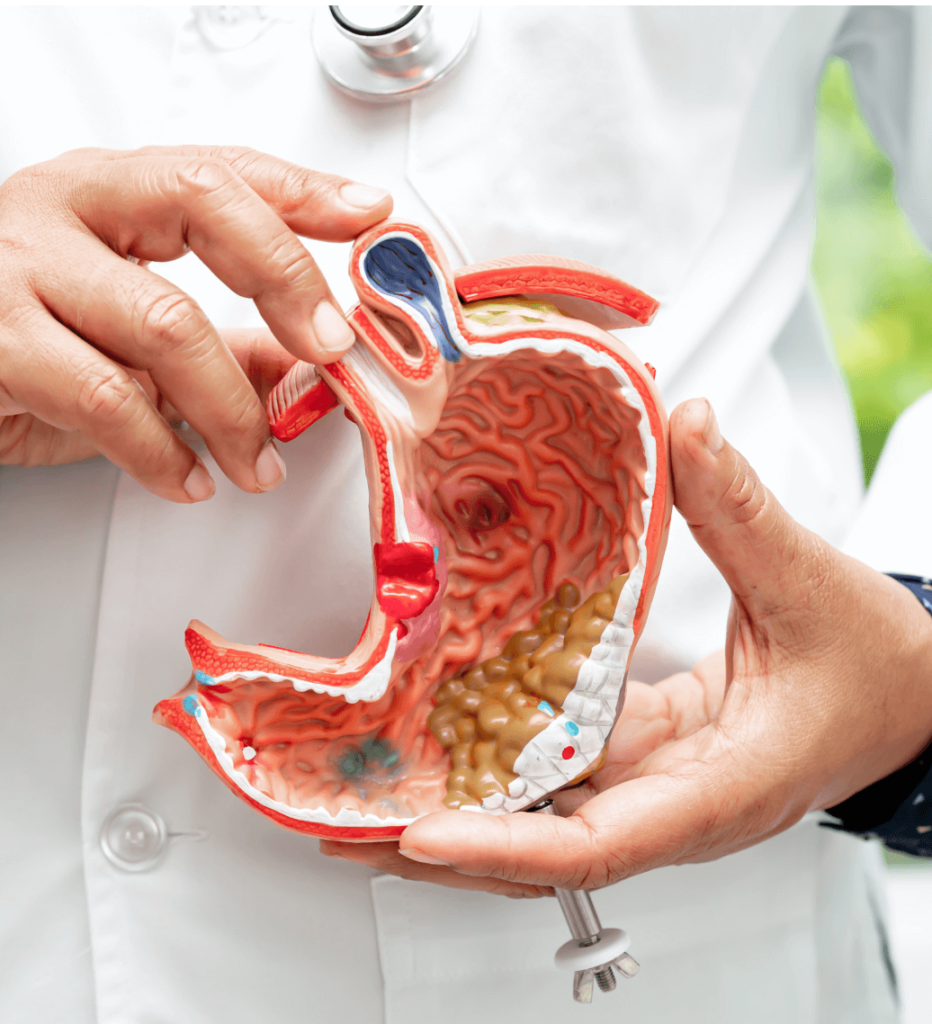
Risk Factors
Helicobacter pylori Infection
Chronic infection with this bacterium is a significant risk factor.
Diet
High intake of salted, smoked, and pickled foods.
Smoking
Increases the risk of gastric cancer.
Family History
Genetics play a role; having a family history of gastric cancer increases risk.
Age and Gender
More common in older adults and men.
Medical Conditions
Chronic gastritis, pernicious anaemia, and stomach polyps.
Previous Stomach Surgery
Such as surgery for ulcers.
SYMPTOMS
Early Stages
Often asymptomatic or nonspecific symptoms such as indigestion, heartburn, or mild stomach discomfort.
Advanced Stages
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Feeling full after eating small amounts of food.
- Vomiting blood or passing black, tarry stools (indicating bleeding).
- Fatigue and weakness.
Trusted for care
Dr Wang and his team are respected and trusted for the care provided to their patients
DIAGNOSIS
Physical Examination and Medical History
Assessing symptoms and risk factors.
Endoscopy
A thin tube with a camera (endoscope) is passed down the throat to examine the stomach lining and take biopsy samples.
Imaging Tests
- CT Scan: To determine the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread.
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): To assess the depth of tumour invasion and involvement of nearby lymph nodes.
- PET Scan: To detect metastasis.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Subtotal (Partial) Gastrectomy
Removal of the part of the stomach affected by cancer.
Total Gastrectomy
Removal of the entire stomach, with the oesophagus connected directly to the small intestine.
Lymph Node Dissection
Removal of nearby lymph nodes to check for cancer spread.
Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
High-energy beams target and kill cancer cells, often used before or after surgery.
Chemotherapy
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
Given before surgery to shrink the tumour.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Given after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Combination Chemotherapy
Using multiple drugs to increase effectiveness.
Targeted Therapy
HER2-Positive Gastric Cancer
Treated with trastuzumab (Herceptin) that targets the HER2 protein.
Other Targeted Drugs
Ramucirumab (Cyramza) for advanced gastric cancer.
Immunotherapy
Checkpoint Inhibitors
Such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) for tumours with specific genetic features (microsatellite instability-high or mismatch repair deficiency).

Palliative Care
Focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life for patients with advanced gastric cancer.
- Pain Management: Medications and other interventions to manage pain.
- Nutritional Support: Working with a dietitian to manage dietary needs and symptoms like nausea.
- Emotional Support: Counselling, support groups, and mental health care.
Follow-Up Care
- Regular Monitoring: Follow-up appointments and imaging tests to monitor for recurrence.
- Managing Side Effects: Addressing side effects of treatment and ensuring overall well-being.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco smoking, and limiting alcohol intake.

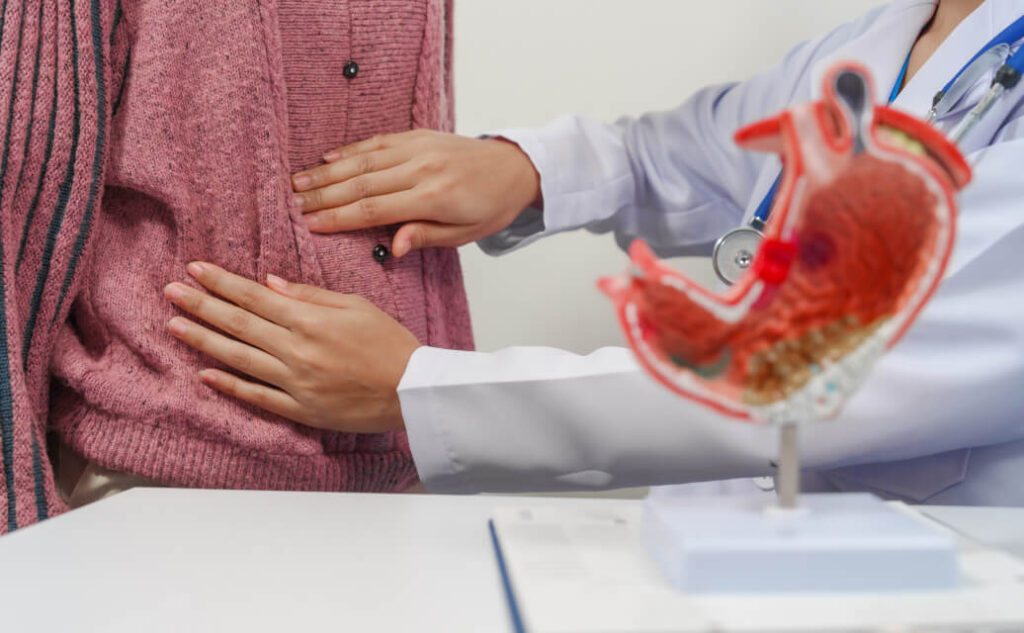
When to Seek Medical Attention
- New or worsening symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or difficulty swallowing.
- Signs of infection such as fever, redness, or swelling at the surgical site.
- Unexplained weight loss or changes in appetite.
Other Upper GI Conditions
Medical procedure used to examine the upper part of the GI Tract, colon and rectum for abnormalities….
Pancreatic cancer begins in the tissues of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach…
Also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining…

Also known as stomach cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining…
